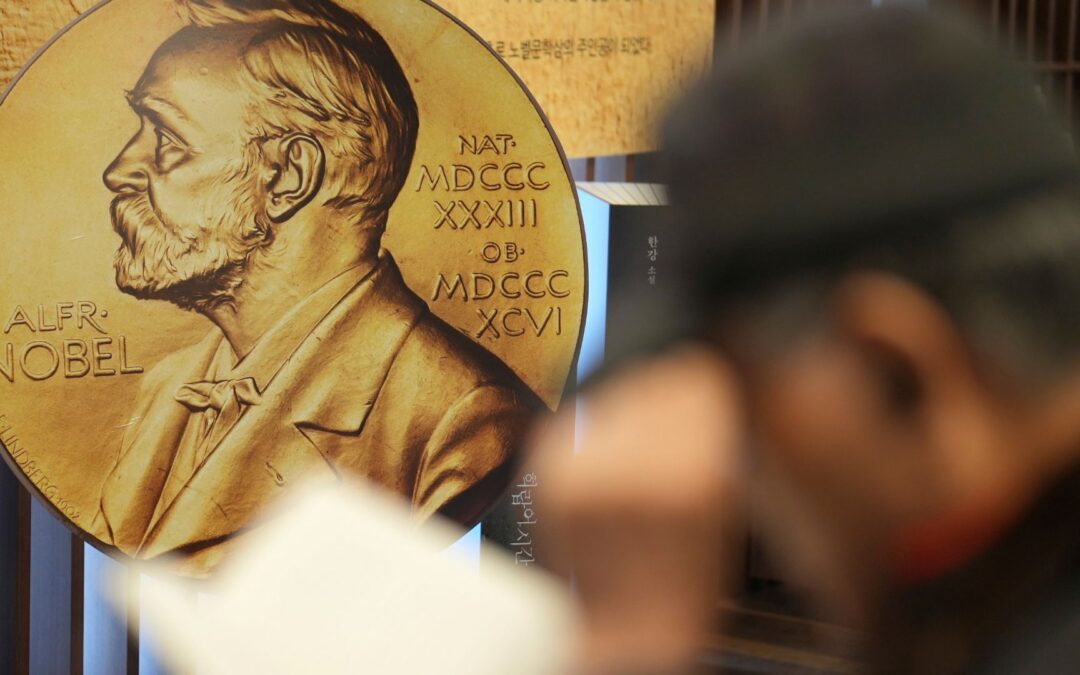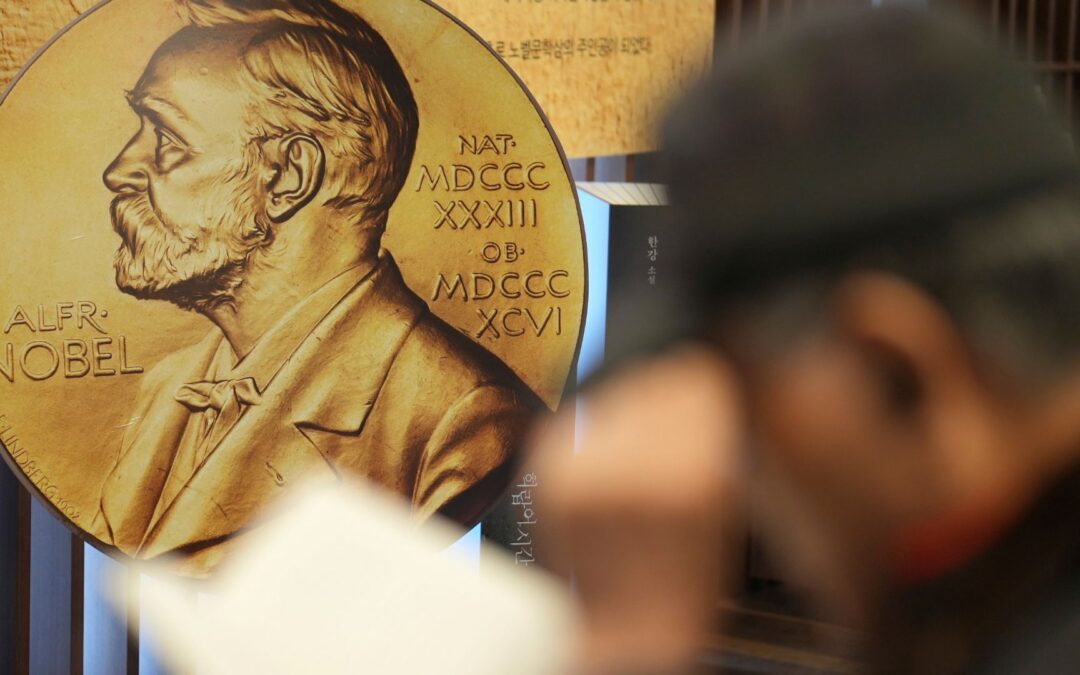
by Robyn Bolton | Oct 13, 2025 | Innovation, Leading Through Uncertainty
As a kid, you’re taught that when you’re lost, stay put and wait for rescue. Most executives are following that advice right now—sitting tight amid uncertainty, hoping someone saves them from having to make hard choices and take innovation risk.
This year’s Nobel Prize winners in Economics have bad news: there is no rescue coming. Joel Mokyr, Philippe Aghion, and Peter Howitt demonstrated that disruption happens whether you participate or not. Freezing innovation investments doesn’t reduce innovation risk. It guarantees competitors destroy you while you stand still.
They also have good news: innovation follows predictable patterns based on competitive dynamics, offering a framework for making smarter investment decisions.
How We Turned Stagnation into a System for Growth
For 99.9% of human history, economic growth was essentially zero. There were occasional bursts of innovation, like the printing press, windmills, and mechanical clocks, but growth always stopped.
200 years ago, that changed. Mokyr identified that the Industrial Revolution created systems connecting two types of knowledge: Propositional knowledge (understanding why things work) and Prescriptive knowledge (practical instructions for how to execute).
Before the Industrial Revolution, these existed separately. Philosophers theorized. Artisans tinkered. Neither could build on the other’s work. But the Enlightenment created feedback loops between theory and practice allowing countries like Britain to thrive because they had people who could translate theory into commercial products.
Innovation became a system, not an accident.
Why We Need Creative Destruction
Every year in the US, 10% of companies go out of business and nearly as many are created. This phenomenon of creative destruction, where companies and jobs constantly disappear and are replaced, was identified in 1942. Fifty years later, Aghion and Howitt built a mathematical model proving its required for growth.
Their research also lays bare some hard truths:
- Creative destruction is constant and unavoidable. Cutting your innovation budget does not pause the game. It forfeits your position. Competitors are investing in R&D right now and their innovations will disrupt yours whether you participate or not.
- Competitive position predicts innovation investments. Neck-to-neck competitors invest heavily in innovation because it’s their only path to the top. Market leaders cut back and coast while laggards don’t have the funds to catch-up. Both under-invest and lose.
- Innovation creates winners and losers. Creative destruction leads to job destruction as work shifts from old products and skills to new ones. You can’t innovate and protect every job but you can (and should) help the people affected.
Ultimately, creative destruction drives sustained growth. It is painful and scary, but without it, economies and society stagnate. Ignore it at your peril. Work with it and prosper.
From Prize-winning to Revenue-generating
Even though you’re not collecting the one million Euro prize, these insights can still boost your bottom line if you:
- Connect your Why teams with your How teams. Too often, Why teams like Strategy, Innovation, and R&D, chuck the ball over the wall to the How teams in Operations, Sales, Supply Chain, and front-line operations. Instead, connect them early and often and ensure the feedback loop that drives growth
- Check your R&D and innovation investments. Are your R&D and innovation investments consistent with your strategic priorities or your competitive position? What are your investments communicating to your competitors? It’s likely that that “conserving cash” is actually coasting and ceding share.
- Invest in your people and be honest with them. Your employees aren’t dumb. They know that new technologies are going to change and eliminate jobs. Pretending that won’t happen destroys trust and creates resistance that kills innovation. Tell employees the truth early, then support them generously through transitions.
What’s Your Choice?
Playing it safe guarantees the historical default: stagnation. The 2025 Nobel Prize winners proved sustained growth requires building innovation systems and embracing creative destruction.
The only question is whether you will participate or stagnate.
by Robyn Bolton | Sep 30, 2025 | Leading Through Uncertainty, Strategy, Tips, Tricks, & Tools
Just as we got used to VUCA (volatile, uncertain, complex, ambiguous) futurists now claim “the world is BANI now.” BANI (brittle, anxious, nonlinear, incomprehensible) is much worse than VUCA and reflects “the fractured, unpredictable state of the modern world.”
Not to get too Gen X on the futurists who coined and are spreading this term but…shut up.
Is the world fractured and unpredictable? Yes.
Does it feel brittle? Are we more anxious than ever? Are things changing at exponential speed, requiring nonlinear responses? Does the world feel incomprehensible? Yes, to all.
Naming a problem is the first step in solving it. The second step is falling in love with the problem so that we become laser focused on solving it. BANI does the first but fails at the second. It wallows in the problem without proposing a path forward. And as the sign says, “Ain’t nobody got time for this.”
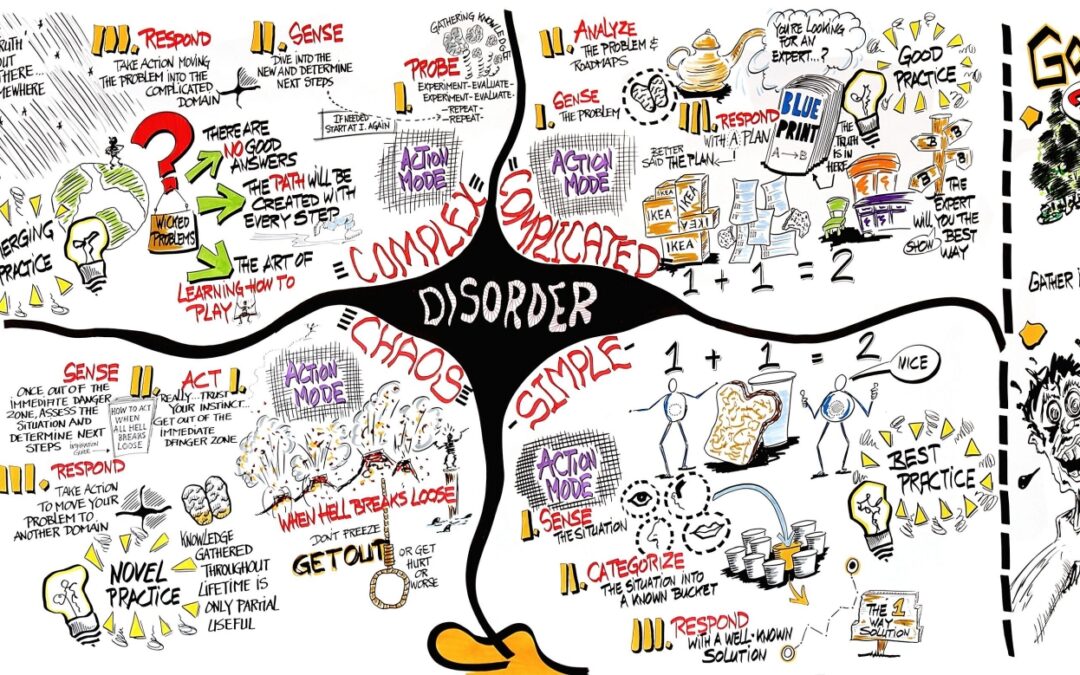
(Re)Introducing the Cynefin Framework
The Cynefin framework recognizes that leadership and problem-solving must be contextual to be effective. Using the Welsh word for “habitat,” the framework is a tool to understand and name the context of a situation and identify the approaches best suited for managing or solving the situation.
It’s grounded in the idea that every context – situation, challenge, problem, opportunity – exists somewhere on a spectrum between Ordered and Unordered. At the Ordered end of the spectrum, cause and affect are obvious and immediate and the path forward is based on objective, immutable facts. Unordered contexts, however, have no obvious or immediate relationship between cause and effect and moving forward requires people to recognize patterns as they emerge.
Both VUCA and BANI point out the obvious – we’re spending more time on the Unordered end of the spectrum than ever. Unlike the acronyms, Cynefin helps leaders decide and act.
5 Contexts. 5 Ways Forward
The Cynefin framework identifies five contexts, each with its own best practices for making decisions and progress.
On the Ordered end of the spectrum:
- Simple contexts are characterized by stability and obvious and undisputed right answers. Here, patterns repeat, and events are consistent. This is where leaders rely on best practices to inform decisions and delegation, and direct communication to move their teams forward.
- Complicated contexts have many possible right answers and the relationship between cause and effect isn’t known but can be discovered. Here, leaders need to rely on diverse expertise and be particularly attuned to conflicting advice and novel ideas to avoid making decisions based on outdated experience.
On the Unordered end of the spectrum:
- Complex contexts are filled with unknown unknowns, many competing ideas, and unpredictable cause and effects. The most effective leadership approach in this context is one that is deeply uncomfortable for most leaders but familiar to innovators – letting patterns emerge. Using small-scale experiments and high levels of collaboration, diversity, and dissent, leaders can accelerate pattern-recognition and place smart bets.
- Chaos are contexts fraught with tension. There are no right answers or clear cause and effect. There are too many decisions to make and not enough time. Here, leaders often freeze or make big bold decisions. Neither is wise. Instead, leaders need to think like emergency responders and rapidly response to re-establish order where possible to bring the situation into a Complex state, rather than trying to solve everything at once.
The final context is Disorder. Here leaders argue, multiple perspectives fight for dominance, and the organization is divided into fractions. Resolution requires breaking the context down into smaller parts that fit one of the four previous contexts and addressing them accordingly.
The Only Way Out is Through
Our VUCA/BANI world isn’t going to get any simpler or easier. And fighting it, freezing, or fleeing isn’t going to solve anything. Organizations need leaders with the courage to move forward and the wisdom and flexibility to do so in a way that is contextually appropriate. Cynefin is their map.

by Robyn Bolton | Sep 2, 2025 | Leading Through Uncertainty, Strategy
In September 2011, the English language officially died. That was the month that the Oxford English Dictionary, long regarded as the accepted authority on the English language published an update in which “literally” also meant figuratively. By 2016, every other major dictionary had followed suit.
The justification was simple: “literally” has been used to mean “figuratively” since 1769. Citing examples from Louisa May Alcott’s Little Women, Charles Dickens’ David Copperfield, Charlotte Bronte’s Jane Eyre, and F. Scott Fitzgerald’s The Great Gatsby, they claimed they were simply reflecting the evolution of a living language.
What utter twaddle.
Without a common understanding of a word’s meaning, we create our own definitions which lead to secret expectations, and eventually chaos.
And not just interpersonally. It can affect entire economies.
Maybe the state of the US economy is just a misunderstanding
Uncertainty.
We’re hearing and saying that word a lot lately. Whether it’s in reference to tariffs, interest rates, immigration, or customer spending, it’s hard to go a single day without “uncertainty” popping up somewhere in your life.
But are we really talking about “uncertainty?”
Uncertainty and Risk are not the same.
The notion of risk and uncertainty was first formally introduced into economics in 1921 when Frank Knight, one of the founders of the Chicago school of economics, published his dissertation Risk, Uncertainty and Profit. In the 114 since, economists and academics continued to enhance, refine, and debate his definitions and their implications.
Out here in the real world, most businesspeople use them as synonyms meaning “bad things to be avoided at all costs.”
But they’re not synonyms. They have distinct meanings, different paths to resolution, and dramatically different outcomes.
Risk can be measured and/or calculated.
Uncertainty cannot be measured or calculated
The impact of tariffs, interest rates, changes in visa availability, and customer spending can all be modeled and quantified.
So it’s NOT uncertainty that’s “paralyzing” employers. It’s risk!
Not so fast my friend.
Not all Uncertainties are the same
According to Knight, Uncertainty drives profit because it connects “with the exercise of judgment or the formation of those opinions as to the future course of events, which…actually guide most of our conduct.”
So while we can model, calculate, and measure tariffs, interest rates, and other market dynamics, the probability of each outcome is unknown. Thus, our response requires judgment.
Sometimes.
Because not all uncertainties are the same.
The Unknown (also known as “uncertainty based on ignorance”) exists when there is a “lack of information which would be necessary to make decisions with certain outcomes.”
The Unknowable (“uncertainty based on ambiguity”) exists when “an ongoing stream [of information] supports several different meanings at the same time.”
Put simply, if getting more data makes the answer obvious, we’re facing the Unknown and waiting, learning, or modeling different outcomes can move us closer to resolution. If more data isn’t helpful because it will continue to point to different, equally plausible, solutions, you’re facing the Unknowable.
So what (and why did you drag us through your literally/figuratively rant)?
If you want to get unstuck – whether it’s a project, a proposal, a team, or an entire business, you first need to be clear about what you’re facing.
If it’s a Risk, model it, measure it, make a decision, move forward.
If it’s an uncertainty, what kind is it?
If it’s Unknown, decide when to decide, ask questions, gather data, then, when the time comes, decide and move forward
If it’s Unknowable, decide how to decide then put your big kid pants on, have the honest and tough conversations, negotiate, make a decision, and move on.
I mean that literally.

by Robyn Bolton | Aug 27, 2025 | Leadership
Imagine that you are the CEO working with your CHRO on a succession plan. Both the CFO and COO are natural candidates, and both are, on paper, equally qualified and effective.
The CFO distinguishes herself by consistently working with colleagues to find creative solutions to business issues, even if it isn’t the optimal solution financially, and inspiring them with her vision of the future. She attracts top talent and builds strong relationships with investors who trust her strategic judgment. However, she sometimes struggles with day-to-day details and can be inconsistent in her communication with direct reports.
The COO inspires deep loyalty from his team through consistent execution and reliability. People turn down better offers to stay because they trust his systematic approach, flawless delivery, and deep commitment to developing people. However, his vision rarely extends beyond “do things better,” rigidly adhering to established processes and shutting down difficult conversations with peers when change is needed.
Who so you choose?
The COO feels like the safer bet, especially in uncertain times, given his track record of proven execution, loyal teams, and predictable results. While the CFO feels riskier because she’s brilliant but inconsistent, visionary but scattered.
It’s not an easy question to answer.
Most people default to “It depends.”
It doesn’t depend.
It doesn’t “depend,” because being CEO is a leadership role and only the CFO demonstrates leadership behaviors. The COO, on the other hand, is a fantastic manager, exactly the kind of person you want and need in the COO role. But he’s not the leader a company needs, no matter how stable or uncertain the environment.
Yet we all struggle with this choice because we’ve made “leadership” and “management” synonyms. Companies no longer have “senior management teams,” they have “senior/executive leadership teams.” People moving from independent contributor roles to oversee teams are trained in “people leadership,” not “team management” (even though the curriculum is still largely the same).
But leadership and management are two fundamentally different things.
Leader OR Manager?
There are lots of definitions of both leaders and managers, so let’s go back to the “original” distinction as defined by Warren Bennis in his 1987 classic On Becoming a Leader
| Leaders |
Managers |
| · Do the right things
· Challenge the status quo
· Innovate
· Develops
· Focuses on people
· Relies on trust
· Has a long-range perspective
· Asks what and why
· Has an eye on the horizon |
· Do things right
· Accept the status quo
· Administers
· Maintains
· Focuses on systems and structures
· Relies on control
· Has a short-range view
· Asks how and when
· Has an eye on the bottom line |
In a nutshell: leaders inspire people to create change and pursue a vision while managers control systems to maintain operations and deliver results.
Leaders AND Managers!
Although the roles of leaders and managers are different, it doesn’t mean that the person who fills those roles is capable of only one or the other. I’ve worked with dozens of people who are phenomenal managers AND leaders and they are as inspiring as they are effective.
But not everyone can play both roles and it can be painful, even toxic, when we ask managers to take on leadership roles and vice versa. This is the problem with labeling everything outside of individual contributor roles as “leadership.”
When we designate something as a “people leadership” role and someone does an outstanding job of managing his team, we believe he’s a leader and promote him to a true leadership role (which rarely ends well). Conversely, when we see someone displaying leadership qualities and promote her into “people leadership,” we may be shocked and disappointed when she struggles to manage as effortlessly as she inspires.
The Bottom Line
Leadership and Management aren’t the same thing, but they are both essential to an organization’s success. They key is putting the right people in the right roles and celebrating their unique capabilities and contributions.

by Robyn Bolton | Aug 13, 2025 | Speaking