
Is Your Brain Friend or Foe? Make It Your Friend with Positive Intelligence
“If you spend a lot of time in your own head, you’re spending time in a bad neighborhood.”
I was deep in a bit of worry and self-doubt when my friend uttered that sentence. Immediately, my mind conjured an image of falling gown building, boarded up doors and windows, overgrown yards, and empty streets (basically downtown Cleveland in the 1980s).
“Man, I do not want to be here!” I said, probably a bit too loudly.
Everyone I know spends a lot of time in their bad neighborhoods. It’s a consequence of the world we live in – more demands, responsibilities, and expectations running into greater uncertainty, fewer options, and weaker safety nets.
There are lots of ways to spruce up our neighborhoods, cultivating a Growth Mindset is one. In his book, Positive Intelligence: Why Only 20% of Teams and Individuals Achieve Their True Potential and How You Can Achieve Yours, author and executive coach Shirzad Chamine, lays out a powerful framework and action plan to build your Positive Intelligence by increasing your PQ (Positive Intelligence Quotient).
Why Should I Care about Positive Intelligence?
Because research proves that a high PQ creates better results
- An analysis of more than 200 different scientific studies, which collectively tested more than 275,000 people, conduced that higher PQ leads to higher salary and greater success in the arenas of work, marriage, health, sociability, friendship, and creativity
- Salespeople with higher PQ sell 37% more than their lower-PQ peers
- Project teams managed by high-PQ managers perform 31% better
- Doctors with a high PQ make accurate diagnoses 19% faster
- People who demonstrated high PQ in their 20s (as evidence by journal entries) live, on average, 10 years longer
Better sales, better performance, better health, longer lives.
Seems like something worth learning more about.
What is Positive Intelligence and PQ?
Chamine defines Positive Intelligence as “an indication of the control you have over your own mind and how well your mind acts in your best interest.” Basically, what kind of neighborhood is your mind.
PQ, your Positive Intelligence Quotient, is “the percentage of your time your mind is acting as your friend rather than your enemy.” It’s expressed on a scale of 0 to 100 and research shows that a PQ of 75 (meaning your mind is your friend, or a good neighborhood, 75% of the time) is a tipping point. “Above it, you are generally being uplifted by the internal dynamics of the mind, below it you are constantly being dragged down by those dynamics.” 80% of teams and individuals score below the tipping point.
How you can increase your PQ
People with high PQs use one or more of the following 3 strategies:
STRATEGY 1 – Weaken your Saboteurs:
Saboteurs, also called Inner Critics, are the voices, beliefs, and assumptions in your head that work against you.
There are 10 and every person has at least two actively chattering away
- Judge: The “Master” Saboteur in everyone’s head. It constantly finds faults in you, others, your circumstances, and anything else it can get its hands on.
- Avoider: Focuses on the positive and pleasant to avoid dealing with difficult and unpleasant tasks, conflicts, and people.
- Controller: Takes charge, seeking to bend people to its will because it believes that the only way to get the best outcomes from people and situations is to control them
- Hyper-Achiever: Relies on constant external rewards, recognition, and praise as a way to feel self-respect and self-validation
- Hyper-Rational: Focuses on logic and reason as the sole means through which to understand people and situations, often leading to impatience or outright dismissal of anything or person deemed not logical
- Hyper-Vigilant: Sees threats in every moment and is constantly on guard and preparing for the worst-case scenario
- Pleaser: Seeks to gain acceptance and affection by constantly helping, pleasing, rescuing, or flattering others
- Restless: Searches for the next adventure, new thing, or adrenaline rush and distracts from the relationships and work that really matter
- Stickler: Needs perfection, order, and organization to such an extent that it makes everyone anxious and uptight
- Victim: Gains attention and affection by focusing on internal feelings, especially negatives ones
To weaken your saboteurs, first identify which one is currently active, then recognize the story its telling you (often, the story will seem helpful so this part is tricky), and then either call it out (“oh, it’s you again, making up stories) or thank it (“thank you for trying to keep me safe. I’ve got this.”)
STRATEGY 2 – Strengthen your Sage:
The Sage perspective is essentially the opposite of the Judge. Whereas the Judge finds everything that is (or could be wrong), the Sage accepts every single thing as a gift or opportunity.
OK, I know this sounds like some new-age woo, especially in the midst of COVID-19 and its impact on every single thing in our lives. Chamine’s C-Suite clients are skeptical of this too, which is why he teaches them the Three Gifts technique – write down the horrible thing then write down 3 ways it could turn out to be a gift or opportunity at some point in the future.
You can strengthen your Sage by using one (or more) of its 5 powers:
- Empathize: When strong feelings are involved and emotional reserves are running low, picture yourself, or the person or situation causing problems, as a small child and interact with it
- Explore: When the situation is complex or you want more information before making a decision, pretend to be a fascinated anthropologist and seek out info by asking questions
- Innovate: When the usual answers aren’t working, adopt an innovator’s mentality greet ideas with “yes….and….”
- Navigate: When faced with multiple options, “flash forward” and imagine yourself at some point in the distant future after having taken each path and consider how you feel in that future place
- Activate: When your Saboteurs are in control, preempt them by writing down everything they could say and recognize, respond, and thank it.
STRATEGY 3 – Strengthen your PQ brain
Your PQ brain is comprised of the middle prefrontal cortex, the right brain, the mirror neuron system, the ACC, and the Insular Cortex (these last three areas control your empathy reaction).
Strengthening your PQ brain is as “simple” as focusing all of your attention on your physical body and/or the experience of at least one of your 5 senses, for at least 10 seconds 100 separate times per day for 21 straight days
Yes, 100 times per days sounds like a lot, so Chamine offers some tip:
- During Daily routines, for example when you’re brushing your teeth, focus on the feeling of the toothbrush against your gums
- While working out
- Before or when you’re eating
- As you listen to music
- When you’re playing sports (including e-sports)
- Being with friends and family
Bottom Line
The data proves that Positive Intelligence has a real and tangible impact on your performance at work, in your relationships, and in life. This book contains a variety of case stories to show the power of Positive Intelligence in action. Even better, it offers an easy to understand framework and totally do-able approach to make Positive Intelligence work for you.
***
To learn more about Positive Intelligence, visit Shirzad Chamine’s site here.
To buy the book, visit you can buy it from independent online bookstores Bookshop or IndieBound, or at Amazon or Barnes & Noble.

How Looking at Art Can Make You a Better Thinker, Communicator, and Leader
“It was quite a sight! A dozen senior executives from a big, conservative financial services firm, all sitting on the floor in front of a painting, talking about what it could mean and why they think that.”
On a typical dreary November day, and Suzi and I were sitting in the café inside Boston’s Museum of Fine Arts. She had just left her job as Head of Design Thinking at Fidelity Investments and I was taking a sabbatical before deciding what would be next for my career. Introduced by a mutual friend, we decided to swap stories over lunch and a walk through one of the museum’s special exhibitions.
She was describing a Visual Thinking (VTS) session she had recently facilitated and the nearly instant impact it had on the way executives expressed themselves and communicated with each other. She saw them engage in a level of creative problem-solving and critical thinking that they hadn’t in the past.
Intrigued, I set off to learn more. What I discovered was a powerful, proven, and gasp fun way to help my clients navigate the ambiguous early days of innovation and embrace their inner curiosity and creativity.
Why should you care about VTS?
Imagine someone says to you, “If you and your team spend 1-2 hours with me each month for 9 months, I guarantee an improvement in your abilities to:
- Quickly gather and synthesize accurate and unique insights by listening deeply and re-phrasing what they heard ensure understanding
- Think critically and creatively by examining information or an idea from all angles, rethinking it, and deciding whether to keep, revise, or discard it
- Communicate more clearly, respectfully, and productively with a variety of people inside and outside the organization
- Work cross-functionally because they can apply critical thinking skills confidently to topics outside of their expertise
- Innovate and experiment because they have learned how to individually and as a team operate in uncertainty
- Provide more effective feedback by phrasing criticisms as questions and engaging in collaborative discovery and problem-solving conversations
Would you make the time commitment?
Now, what if they said, “All you have to do each month is sit together in a conference room and take part in a conversation. No travel. No additional expenses. Just turn off your email and your phone for one hour and have a conversation in a room you already pay rent on.”
Would you do it then?
Of course you would.
Because you’ve been to trainings that focus on only one of the items in the list above and those trainings are expensive, time-consuming, and not nearly as effective as they should be.
What is Visual Thinking Strategies (VTS)?
According to the book, Visual Thinking Strategies: Using Art to Deepen Learning Across School Disciplines, VTS “uses art to teach visual literacy, thinking, and communication skills – listening an expressing oneself.”
Philip Yenawine was the Director of Education at the Museum of Modern Art (MOMA) in New York from 1983 – 1993. During that time, he noticed that despite the museum’s efforts to organize and craft detailed explanations and interpretations for each piece of art, visitors would still ask lots of “Why?” questions and would remember little, if anything, from their visit.
Frustrated but curious, he and his team began studying developmental research and theory and discovered that what MOMA visitors needed wasn’t explanations, details, and facts, it was “permission to be puzzled and to think. Consent to use their powerful eyes and intelligent minds. Time to noodle and figure things out. The go-ahead to use what they already know to reflect on what they don’t; the first steps of learning.”
Philip and his team with MOMA partnered with cognitive psychologist Abigail Housen to develop and test a process now known as Visual Thinking Strategies (VTS).
In the 30 years since their initial experiments, Philip and Abigail’s work has been used in 28 countries and 58 museums, over 12,000 students have engaged in VTS discussions and 1,200 people have become trained facilitators.
How to do VTS
The secret to VTS’ effectiveness is in the facilitation so if you’re going to do this, invest in an expert facilitator. An expert facilitator is the only way to get the results listed above.
Here’s how a VTS session works:
- Facilitator shares a piece of art specially selected so that “the subjects are familiar… but they also contain elements of mystery.”
- Attendees take one minute to silently focus on the art
- Facilitator asks 3 questions over the hour:
- What’s going on in this picture?
- What do you see that makes you say that?
- What more can you find?
- As each individual answers a question, the Facilitator:
- Points at what is being observed
- Paraphrases what has been said
- Links what has been said to what others have said
- Facilitator wraps up the session by thanking everyone and sharing something s/he learned from listening. They do NOT give “the answer” because “this isn’t about right and wrong but about thinking and…that the students singly and together are capable of wonderful, grounded ideas.”
That’s it – 1 piece of art, 3 questions, and at least 5 major benefits if you commit to the process.
Seems like something worth sitting on an art gallery floor for, right?
To learn more, read Visual Thinking Strategies: Using Art to Deepen Learning Across School Disciplines by Philip Yenawine and visit the website Visual Thinking Strategies

The Intrapreneur, Confessions of a Corporate Insurgent
When I first heard about this book, a first-person account of innovating within a large corporation, and that it was set in a mental hospital, I thought “Yup, sounds about right.”
The craziest, most inspiring, and strongest people I have ever known are intrapreneurs. Because you have to be crazy to believe that you can change a massive organization, you have to inspire others to follow you into the fight, and you have to be strong to withstand near-constant defeat and, if and when success arrives, shine the spotlight no on yourself but on all the people who fought alongside you.
Gib’s story is similar to those of other Intrapreneurs.
He was in his early-30s and only a few years into his tenure at Accenture when he proposed the creation of Accenture Development Partnerships based on his experience working with Voluntary Service Overseas (VSO), a program in which business professionals would be loaned out by their employers (who would hold their jobs for 6–12 months) to work as volunteers in developing countries. Corporate social Responsibility (CSR) was all the rage at the time and, Gib reasoned, Accenture was well positioned to replicate VSO’s model given its global staff of bright young consultants and list of clients eager to appear to do good in the world.
The next 15 years were a roller-coaster, one familiar to anyone who has tried to innovate in a corporate environment. The ups of getting support, seeing things work, and watching change unfold. The downs of losing champions, justifying your existence, and fighting to maintain your meager resources despite phenomenal results. The ride ended not with a return to the station (aka a quiet role back in the core business) but with a four-day stay at a psychiatric hospital when his friends and family became concerned about his manic energy and fixation on creating a “Fourth Sector” that would combine the best of the public (government), private (business), and third (NGO) sectors to serve humanity’s greatest needs.
3 Profoundly True and Important Messages
Even though his story is one I lived early in my career, when I was an intrapreneur at P&G, and one that, as a corporate innovation consultant, I’ve seen others live, there were three passages in the book that I found so profoundly important and true that they simply must be shared
Innovation, and lack thereof, is a leadership problem.
“At its core, the problem is about leadership. Too many people believe leadership comes as the result of a promotion — or from a fancy job title on a business card. Not at all. Leadership is more of a mindset than a skillset. Leaders can emerge at all levels of an organisation, even low down.”
Corporate antibodies are the #1 killer of innovation
(Reflecting on an unsupportive executive):
“(Executive) was old school leadership. He’d climbed the ladder in the Business 1.0 world. He was programmed to have a single-minded focus on the business fundamentals — an entire career spent cutting cost, growing revenues, driving efficiency. What’s the problem with that? You might ask. It certainly worked for him, and he’d reached the heady heights of the senior management ranks.”
(When asked it this executive was the main problem):
“Yes and no. We also got confronted by legal, tax, compliance, security, you name it. My team bore the brunt of their endless checks, audits, and bureaucracy. I remember having a very strong feeling that we were suffering from a thousand cuts and I was powerless to do anything. Good people were leaving our team out of sheer frustration or pressure.”
Intrapreneurs are the heroes this world needs
“Intrapreneurs are not content with business as usual and aspire to drive change bottom up and inside out of their own organisations. These are the people who won’t change companies when they get frustrated in their jobs or crave more purpose from their careers. Instead, they stay put and change the companies they’re in….
No one ever said it would be easy. Of course it’s risky for your career. Sure, you’ll be laughed at. Told you’re crazy. Overlooked for promotion. Yes, you might even lose your job. I often think of the reactions that a Picasso or a Jackson Pollock must have had when they shared their first works of art. Or how silly that first person trying to start a Mexican wave must have felt when they stood up screaming with their hands in the air, only to find they were the only one. My point is that you may have to be prepared to appear crazy to others if you’re going to be successful in driving change in any organisation.”
In closing
The Intrapreneur is a good read (though it does get a bit self-congratulatory in parts). Reassuring to other intrapreneurs that they are not alone. Perhaps eye-opening to executives who wonder why their organizations aren’t more innovative. Definitely the story of someone on the edge of sanity. Because all intrapreneurs are.

The Disruption Dilemma
It’s been 22 years since the publication of The Innovator’s Dilemma, the book that catapulted Clayton Christensen to guru status, shocked and scared executives at large companies, and brought innovation into the mainstream.
In the decades since, “innovation,” “disruption,” and a host of related terms have become meaningless buzzwords, a massive industry of consultants and advisors (yes, including Mile Zero) has sprung up, and an untold number of books and articles have been written about how to innovate.
Yet nothing has changed.
Large organizations still struggle to launch anything other than incremental innovations, the failure rate of start-ups remains astoundingly high, and executives continue to flock to the latest innovation trend (2019 seems to be the year of Corporate Venture Capital).
Why?
That’s the question that Joshua Gans, Professor of Strategic Management and holder of the Jeffrey S. Skoll Chair of Technical Innovation and Entrepreneurship at the University of Toronto’s Rotman School of Management, tries to answer in his book The Disruption Dilemma.
He starts by grounding the reader in the core definitions and theories related to disruption, then makes the case that rather than trying to predict disruption (a difficult if not impossible task) organization should instead follow one of four strategies, before wrapping up with a re-examination of the data and research Christensen used to create his original theory of disruption.
“Disruption” is more than a new technology…it is an identity crisis
in their 1995 Harvard Business Review article, “Disruptive Technologies: Catching the Wave,” Clayton Christensen and Joseph L. Bower coined the term “disruptive technology” and defined it as having
“two important characteristics: First they present a different package of performance attributes — one that, at least at the outset are not valued by existing customers. Second, the performance attributes that existing customers do value improve at such a rapid rate that the new technology can later invade those established markets.”
For Christensen. disruption occurs when management chooses not respond to a new innovation because it does not perform as well as existing solutions along traditional performance dimensions and therefore is unappealing to existing customer.
Interestingly, at the same time that Christensen was studying for his PhD at Harvard, another doctoral student was also conducting research into why successful firms fail in light of new technologies. In 1990, Rebecca Henderson, now one of only two University Professors at Harvard (the other one is Michael Porter), debuted the term “Architectural Innovation” with her collaborator, Kim Clark, in their paper “Architectural Innovation: The Reconfiguration of Existing Product Technologies and The Failure of Established Firms.”
For Henderson, disruption, happens when managers are unable to respond because the innovation requires changes to how the firm operates, communicates, coordinates, learns, and makes decisions. Thus,
“Architectural innovation presents established firms with a more subtle challenge. Much of what the firm knows is useful and needs to be applied in the new product but some of what it knows is not only not useful but may actually handicap the firm. Recognizing what is useful and what is not, and acquiring and applying new knowledge when necessary, may be quite difficult for an established firm….”
Gans terms the Christensen theory demand-side disruption and the Henderson theory supply-side disruption. He unites both of these two types of disruption under a single definition of disruption as
“what a firm faces when the choices that once drive a firm’s success now become those that destroy its future.”
What I like about this definition is that it takes disruption beyond the narrow fields of technology, products, or services and considers it in the broader context of markets and industries. It reveals disruption to be something that all organizations are likely to face at some point in their future and one that will call into question many of the fundamental beliefs upon which the organization operates. Further, identifying and understanding both demand- and supply-side disruption can help organizations understand the challenge they face and where and how to focus their resources to navigate the rough road ahead.

Kodak Smile and the Polaroid Mint
Predicting disruption is hard.
What both demand-side Disruption (Christensen) and supply-side Disruption (Henderson) theories have in common is that they are kicked off by the introduction of a new innovation into the market.
However, new innovations launch all the time and very few of them start the domino effect that characterizes disruption. This is because an innovation must do two things in order to be disruptive: (1) offer poorer performance on some dimensions that existing customers value and offer new performance benefits that appeal to new customers and (2) improve rapidly enough that the innovation is able to quickly perform at levels desired by existing customers while offering the new benefits that new customers have grown to love.
As Gans point out, it’s relatively easy to determine if an innovation will meet the first criteria but it takes time to know whether or not the second criteria will be met. “Therefore, both supply- and demand-side theories lead to the conclusion that predicting disruptive events is very challenging, if not impossible.”
Responding is even harder.
To illustrate this point, Gans shares the stories of Polaroid and Kodak, two companies that recognized and responded to a potentially disruptive innovation decades before it transformed the market, but still failed.
In 1981, Polaroid recognized the threat posed by digital technologies. By 1989, it was investing over 40% of its R&D budget into digital imaging. However, while it was investing in technology, it was struggling to envision the right products to commercialize its technological advancement. This struggle was rooted not in its ability to innovate cameras but rather by “razor/blade” business model (and supporting mindset) that resulted in Polaroid subsidizing cameras and making money on film, a model (architecture) that would need to change if the company shifted from film to digital technology.
The company resisted re-organizing itself around the new architecture such that when it eventually developed and launched a digital camera it into the market, there were already 40 established competitors and Polaroid struggled to differentiate itself. Five years later, in 2001, Polaroid declared bankruptcy.
Digital imaging technology had been on Kodak’s radar screen since the mid-1970s. In the 1990s, it partnered with companies like Apple to develop digital cameras and, by 2005, was the market leader in docks that enabled sharing of digital images between computers and cameras.
So prescient were Kodak’s senior executives that “it was even one of the first few companies to consult with Clayton Christensen himself. Managers at Kodak read the Innovator’s Dilemma upon its publication and used it messages to direct Kodak’s product strategy. One example of this was to launch cameras in toy stores as a defense against Nintendo, which had put them in one million Game Boys. Nintendo’s cameras were by all accounts awful, but they were enough to get Kodak worried about disruption. Kodak was able to outpredict the market and to make substantial investments in what came to be disruptive innovations. Though they were initially inferior on multiple dimensions, the improved to take the market in less than a decade.”
If Kodak did everything right, at least according to Christensen’s theory, why did it declare bankruptcy in 2012?
It failed because it did not predict that the dominant design for digital photos would shift from cameras to phones and continued to innovate and invest in “hybrid products that would combine its existing strengths with the new technologies, for example the Photo CD, a way of taking film to photo shops and bringing a digital product home.”
The moral or these stories is that if you are able to identify a potentially disruptive innovation and if you take action to respond, it is nearly impossible to predict the path the innovation will take and attempting to do so is likely to require considerable resources but result in adding only a few years to the organization’s life.
4 strategies for responding to disruption
If you buy-in to Gans’ argument that predicting and trying to stave off disruption is a fool’s errand, it can be tempting to throw up your hands, declare defeat, and simply wait for disruption to claim your organization as its next victim. And, to be fair, Gans does offer this, Wait and Give up, as one of four possible strategies to deal with disruption.
But let’s say you’re not one to declare defeat easily or quickly, what then?
According to Gans, you first need to acknowledge that the two greatest barriers to innovation are uncertainty and cost. Uncertainty is a barrier because, as described above, you can’t be certain of an innovation’s disruptive path until it is well on the journey and this uncertainty is likely to make managers hesitant to take action. However, even if managers are willing to stomach uncertainty, “established firms face a dilemma in introducing new products or innovations because this cannibalizes their existing, profitable businesses….” This reality, “that there are no free lunches, only trade-offs,” has been part of economic theory since Nobel Prize winner Kenneth Arrow named it “the replacement effect” in a 1962 paper.
For organizations unwilling to surrender to disruption, Gans offers three potential strategies to manage uncertainty and cost and position themselves for success:
1. Double Down by leveraging existing strengths to contain a new entrant. This strategy works best when the innovation to which the organization is responding turns out to NOT be disruptive. In cases where it is disruptive, organizations are likely to face the same challenges and fate as Kodak and Polaroid
2. Wait and Double Up by investing heavily only once it is certain that an innovation is disruptive. This approach works because, as economists Richard Gilbert and David Newbury wrote in 1981, “when an established firm can defend a monopoly segment against innovative entry through investment, its incentive to protect its monopoly will be greater than the incentive for new entrants to invade.”
3. Wait and Buy Up a the most promising new entrant. Even though established firms are likely to pay a premium to acquire the new entrant, it offers them certainty of watching the market shake out and saving them the cost of the Double down or Double up strategies. However, this strategy works the best when only market-side (Christensen) disruption is occurring as “the problem faced by established firms is not the acquisition of such knowledge but instead the integration of different ways of doing things into an organization that already has ingrained processes.”
Putting it all into practice
As much fun as it is to nerd-out on innovation theory, let’s get down to brass tacks and outline what all of this means to Intrapreneurs (people trying to innovate within existing organizations).
For me, this boils down to three questions organizations need to ask themselves:
1. Should we act in response to a potential disruption?
2. How should we organize to respond?
3. What should we do to respond?
The questions and their corresponding answers form a basic decision tree:
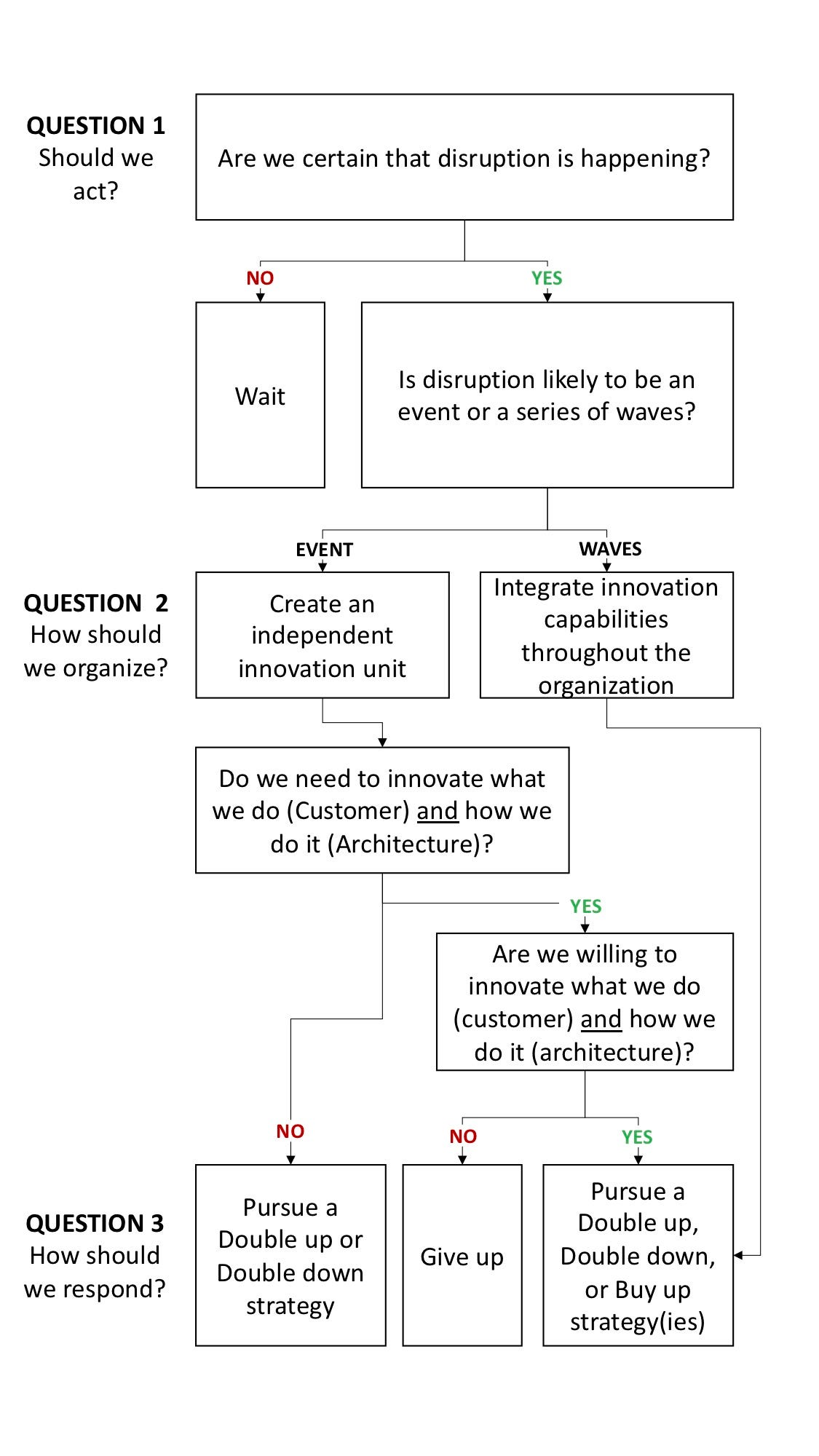
The answers to question 1 were outlined above — large organizations should WAIT until they are certain that disruption is occurring and have confidence in the path it could take
The answers to question 2 reveal another point of difference between Christensen’s and Henderson’s theories:
Christiansen advocates for independent autonomous units, using Lockheed’s famous Skunk Works as an example. He asserts that, in order to be successful, independent units “cannot be forced to compete with projects in the mainstream organization for resources. Because values are the criteria by which prioritization decisions are made, projects that are inconsistent with a company’s mainstream values will naturally be accorded lowest priority. Whether the independent organization is physically separate is less important than is its independence from the normal resource allocation process.” (The Innovator’s Dilemma)
Henderson recommends integration — a culture and practice in which organizations examine and question the implicit linkages in how they operate, evolve them to meet business needs, and readily assimilate linkages that emerge or are acquired. This approach enables firms to respond to both demand- and supply-side disruption. However, “to proactively use integration to prevent disruption often involves sacrificing short-term competitiveness and even market leadership” and, as a result, Gans argued is best used by companies operating in industries where disruption is frequent.
How an organization answers question 3 is based on numerous factors, including available capital, competitive activity, and market/ shareholder pressure. In my experience, however, the choice usually boils down to how the organization has historically grown. Companies that have grown primarily through acquisition should prioritize a Buy up strategy while those that typically grow organically should eschew acquisition for and either Double up or Double Down.
The bottom line
The book wraps up with a nerd-tastic deep dive into Christensen’s research of the micro-processor industry, the data set he used to develop his theory of disruption, and the logic and analysis flaws in his conclusions. It’s worth reading but, as Gans admits, it shouldn’t significantly alter how we think about disruption
Ultimately, by weaving together multiple theories of disruption with tried and true economic theories, The Disruption Dilemma expands how we think and talk about the dynamics that influence if and how organizations respond to disruption and ultimately how we can be more successful when confronting it.

Your Brain At Work by David Rock
“You have power over your mind — not outside events. Realize this, and you will find strength.” Marcus Aurelius
That, in a nutshell, is what Your Brain At Work is all about . By blending snapshot stories, scientific and medical research, and practical examples, David Rock lays out a convincing and easy to read argument that, by understanding the workings and limitations of our brains, we can better understand others, overcome challenges, and navigate our world.
While this book is certainly written for a mass audience, innovators especially should give it a read because of what it has to say about insights, ideas, and driving change.
INSIGHTS
We’ve all had those A-Ha! moments. Those brief seconds when we’re doing nothing of import (like taking a shower) and suddenly, without warning, an insight pops into our heads.
Often those insights are an answer to a question or a solution to a problem that has been plaguing us. We’ve encountered a new challenge and we know that the usual solutions, procedures, and answers won’t work, but we don’t know what will.
What we need is an insight — “not a logical solution,” Rock explains, “but one that recombines knowledge (and maps in your brain) in a whole new way.”
The reason why insights pop into our heads when we’re doing nothing is that our brain is, in fact, doing quite a lot. Studies conducted by Dr. Stellan Ohlsson, at the University of Illinois at Chicago, explain why this is, “when facing a new problem, people apply strategies that worked in prior experience. This works well if the new problem is similar to the old problem. However, in many situations, this is not the case, and the solution from the past gets in the way, stopping better solutions from arising… Instead, the projection of prior experience has to be actively suppressed and inhibited.”
By not thinking of anything in particular, we’re actually suppressing the usual answers and creating space for new answers (insights) to emerge. And luckily, we don’t have to spend our days in the shower to make this happen.
How to Create Insights:
- Focus on the big picture: Dr. Mark Beeman, an associate professor at Northwestern University and an expert in the neuroscience of insights, found that when people solve a problem using insights, their right anterior lobe (a region in the brain’s right hemisphere) becomes more active than usual. Because the right hemisphere is primarily responsible for identifying holistic connections, keeping it active is key to producing insights. However, when we focus on the details of a problem, instead of the big picture, we activate the left hemisphere this decreasing activity in the right hemisphere and reducing the conditions required for insight.
- Get a fresh perspective: As Dr. Ohlsson’s research shows, the more we know about a problem or a situation, the more likely we are to rely on past experience for a solution. It can be incredibly hard to get out of our own way so, instead, we should seek out people with different experiences and perspectives for their input. Even if they don’t have the perfect answer, simply listening to a different perspective can help create the space needed for insights to emerge
- Have fun. Beeman’s research has also revealed a strong correlation between emotional states and insight. As Rock explains, “Increasing happiness increases the likelihood of insight, while increasing anxiety decreases the likelihood of insight. This relates to your ability to perceive subtle signals. When you are anxious, there is greater baseline activation and more overall electrical activity, which makes it harder for you to perceive subtle signals.” Quite simply, if you’re happy, you’re able to pick up subtle pieces of information that can be used to create brilliant insights.
IDEAS
Throughout the book, Rock uses a small theater as a metaphor to explain how the brain works.
Imagine that your pre-frontal cortex, the part of the cortex (the curly gray outer covering of your brain) that sits just behind your forehead and that Is responsible for most of our decision-making and problem-solving activity, is a stage. The stage is small, it can hold only a handful of people at a time, and it needs A LOT of lighting (energy) to operate (think).
In the theater are actors, pieces of information from the outside world, and the audience, information from our internal worlds (thoughts, memories, etc.).
YOU are the director and you can move actors (external info) and audience members (internal info) on or off the stage at any given time to accomplish the following:
- Understand a new idea — put an actor (external info) on the stage and see how it interacts with the audience (info already in your head)
- Make a decision — put several actors on stage and compare them to each other
- Recall information — bring an audience member on stage
- Memorize — move actors off-stage and put them in the audience
- Inhibit thoughts — move actors off stage
Understanding how your brain works, and that you can control it, provides insights into how to get the most out of it on a daily basis AND how to get the most out of others’ brains when you need to — like during an ideation session
How to Generate Better Ideas
- Start in the morning: The pre-frontal cortex is energy-hungry so the more your work it, the more physically and mentally drained you become. Doing creative work early in the day means that you’re starting with all your available energy
- Tell stories about people: When explaining a problem to people, it’s tempting to lay out all the facts. But “studies have shown that when you give people a logic problem to solve, they do so dramatically faster than when the problem is explained in terms of people interacting rather than in terms of disembodied conceptual ideas.” This is why personas, photos, and videos are so powerful during ideation, the move our thinking away from the conceptual (e.g. “how can we increase revenue?”) to the personal (e.g. “how can we better serve Claire the Customer?”)
- Provide diverse, analogous, and unexpected example solutions to spur ideation: “Picturing something you have not yet seen is going to take a lot more energy and effort,” Rock writes. “This partly explains why people spend more time thinking about problems (things they have seen) than solutions (things they have never seen and taking breaks gives you the opportunity to recharge so that you can continue the creative work.” Give people examples of solutions so that they can shift their thinking away from problems AND suppress their instinct to focus on existing solutions to the new problem they’re facing
CHANGE
We’ve all heard the clichés — “Get comfortable being uncomfortable” and “The only thing that is certain is uncertainty” and “The only thing that is constant is change.” But none of them make us feel better when everything around us is changing and, especially when we are being asked to change.
The reason for that is, according to neuroscientists, “because uncertainty feels, to the brain, like a threat to your life.”
It’s easy for innovators, people who feel it is their mission to drive change, to forget this when we propose new ideas or procedures. We are confident that we’ve done the work required to make a thoughtful and correct proposal that improves a product, process, or situation and are dumbfounded when we meet with resistance.
While we’ve worked hard on our idea, we’ve forgotten to work hard to understand how our audience’s brains will react. Specifically, whether the people we are presenting to may experience threats in one or more of the following domains:
- Status: Will I be perceived as less than other people?
- Certainty: Am I being asked to do things differently?
- Autonomy: Will I lose control or decision-making authority?
- Relatedness: Will I lose my connection to others?
- Fairness: Were my expectations not met?
Anticipating possible reactions in any and all of these domains, and addressing them directly or indirectly is critical to creating and sustaining change
How to Create Change
- Proactively address and reduce threats: Act humbly and acknowledge someone’s position and role to reduce threats to status, Set clear expectations and talk openly about the future to increase certainty. Let others own key activities and make timely and clear decisions to promote autonomy. Be authentic and real in all of your communications to reinforce relatedness. Keep your promises and quickly address broken ones in order to promote a perception (and reality) of fairness.
- Set goals and provide rewards: Setting goals as they relate to any of the five items above (stats, certainty, autonomy, relatedness, and fairness) and prime people’s brains to look for evidence that they are progressing towards those goals. Adding in a reward for achieving the goals further improves the likelihood that change will occur because it keeps “the expectation of a primary reward in sight…(which) will lift their moods and improve their thinking.”
- Repeat. Repeat. Repeat: “Real change requires repetition,” explains Rock. You’re asking people to stop doing something they’ve been doing for a long time and to start doing something different. That isn’t going to happen overnight and it’s certainly not going to happen based on even the most compelling data-based argument (how many of us eat as many vegetables, exercise as often, or floss as frequently as we should?). Instead, change happens because we are reminded of it, it is reinforced, and we are rewarded over and over and over again.
In conclusion
These lessons and actions only skim the surface of the interesting and useful insights in Your Brain at Work. But to learn more, you’ll just have to buy it.